Philippines – per capita Fossil CO2 Emissions (zero Climate Debt)
2020
Although the accumulated Climate Debt of the Philippines is zero, the populous country is the world’s 35th largest emitter of Fossil CO2.
The following diagrams expose the trends of Fossil CO2 Emissions, GDP(ppp-$), Forest Cover, Primary Forest and Ecological Footprint without carbon.
Commission on Human Rights of the Philippines accuses Shell, BP, Chevron, BHP Billiton, Anglo American and 42 other carbon companies of breaching people’s fundamental rights to life, food, water, sanitation, adequate housing and self-determination
According to ‘The Guardian’ the Filipino government body ‘Commission on Human Rights of the Philippines‘ have given the world’s largest oil, coal, cement and mining companies 45 days to respond to a ‘legal complaint (pdf, 65 p)‘ that their greenhouse gas emissions have violated the human rights of millions of people living in the Philippines.
The UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights explicitly call on companies to respect human rights, and there are three scenarios in which a company can be hold responsible for adverse impacts on human rights, quote: “(1) it may cause impacts through its own activities; (2) it may contribute to impacts through its own activities, either directly or through some outside entity (government, business, or other); and (3) it may be involved in impacts caused by an entity that is directly linked to its business operations, products, or services.”
New at COP21: The Vulnerable Twenty Group (V20)
2015
Prior to COP21 in Paris in December twenty countries most at risk from the effects of global warming has formed ‘The Vulnerable Twenty Group (V20)’. Unified, the new group hopes for greater access to climate finance for adaptation and mitigation. The twenty countries representing almost one-tenth of the world’s population are: Bangladesh, Philippines, Ethiopia, Vietnam, Tanzania, Kenya, Afghanistan, Nepal, Ghana, Madagascar, Rwanda, Costa Rica, Bhutan, Timor-Leste, Maldives, Barbados, Vanuatu, Saint Lucia, Kiribati and Tuvalu. The first thirteen on the list have full data in ClimatePositions and they are all Contribution Free (no Climate Debt) among 147 countries (see the ‘ranking’). The last seven are examined below in terms of climate change performance.
Climate change performance of Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia and the Philippines
2015
6.4% of the world population lives in Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia or the Philippines – they emitted 3.2% of the global carbon dioxide from fossil fuels in 2012. The four diagrams below show the emissions per capita 2000-2013 (preliminary estimates of 2013) of the four populous countries of which only the Philippines is Contribution Free (no climate debt) in ClimatePositions. The green bars are the Contribution Free Level of CO2 Emissions calculated from emissions in 1990s and a number of continuously updated ‘indicators’.
Climate change performance: Japan vs. South Korea
2014
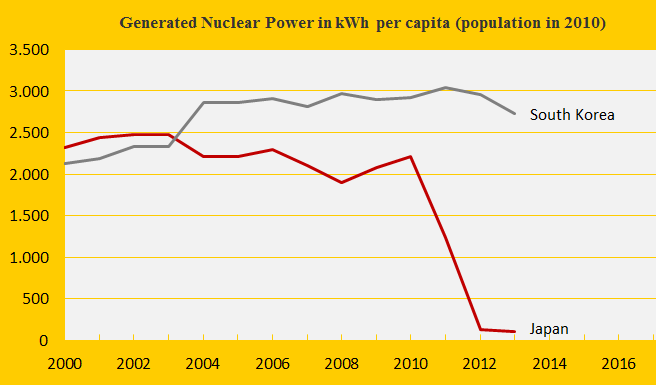
The first diagram shows the nuclear power generation per capita of the two countries. The Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan in 2011 has caused a remarkable shutdown of generation – while CO2 Emissions from the burning of petroleum, coal and natural gas have increased (from 2011 to 2012 respectively by 6%, 5% and 3%) to close the energy gap. Nuclear power generation produce dangerous radioactive waste to deal with for thousands of future generations (10,000 to 250,000 years) and in ClimatePositions nuclear power is not accepted as a national CO2 Emission reduction instrument (read ‘more’). The following analyzes the indicator trends of Japan and South Korea.
The Philippines beats Malaysia in climate change performance (what about the rainforests?)
2014
The Philippines is Contribution Free in ClimatePositions while Malaysia was the 36th worst performing country out of 145 in 2010. In 2014, the Malaysian Climate Contribution (climate debt) increased to $997 per capita and the present ranking is 31st (see ‘here’). The first diagram (below) illustrates the typical correlation between rapid economic growth and loss of sustainability that increases climate debt. The Malaysian climate debt, computed as a percentage of GDP(ppp-$) annually since 2000 increased from 0.38% in 2010 to 0.41% in 2014 (see the ranking ‘here’). This clearly demonstrates the lack of sustainable growth. The following examines the indicators of CO2 Emissions, Ecological Footprint, Forest Area and Marine Protection of the Philippines and Malaysia.