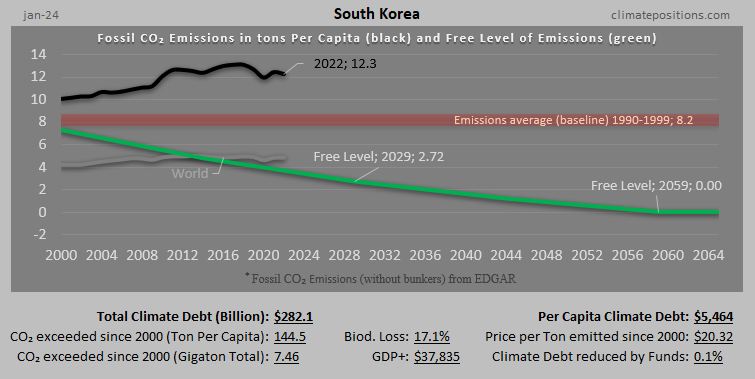
South Korea: Per Capita Climate Debt $5,464 (Ranked 14) – Fossil CO2 Emissions
In 2024, South Korea is responsible for 3.61% of the Global Climate Debt accumulated since 2000. Below are some key figures in the calculations.
Australia – per capita Fossil CO2 Emissions and Climate Debt
2020
Australia’s current Climate Breakdown Pricing amounts to $32.40 per tons Fossil CO2 emitted since 2000. The Climate Debt grew from $6,547 per capita in 2015 to $11,256 in 2020. Updated Rankings of 165 countries are available in the menu “Climate Debt”.
The following diagrams expose the trends of Fossil CO2 Emissions, Climate Debt, GDP(ppp-$) and Ecological Footprint without carbon.
Japan – per capita Fossil CO2 Emissions and Climate Debt
2020
Japan’s current Climate Breakdown Pricing amounts to $20.35 per tons Fossil CO2 emitted since 2000. The Climate Debt grew from $1,952 per capita in 2015 to $3,734 in 2020. Updated Rankings of 165 countries are available in the menu “Climate Debt”.
The following diagrams expose the trends of Fossil CO2 Emissions, Climate Debt, GDP(ppp-$), Nuclear Power and Ecological Footprint without carbon.
Share of global Climate Debt rank 7th, 8th and 9th: South Korea, Australia and Germany (combined responsible for 9% of Climate Debt and 5% of Fossil CO2 Emissions 2016)
2017
The diagram below shows ‘Share of global Climate Debt‘ in 2010, 2015 and 2017 of South Korea, Australia and Germany (ranked 7th, 8th and 9th). The South Korean share is stable over time, Australia’s is decreasing although at a slower rate lately, while Germany’s is increasing.
Share of global Climate Debt rank 4th, 5th and 6th: Canada, Russia and Saudi Arabia (combined responsible for 12% of Climate Debt and 8% of Fossil CO2 Emissions 2016)
2017
The diagram below shows ‘Share of global Climate Debt‘ in 2010, 2015 and 2017 of Canada, Russia and Saudi Arabia (ranked 4th, 5th and 6th). Canada’s share is decreasing, while Russia’s and Saudi Arabia’s are increasing. Global Climate Debt accumulated since 2000 is $7.2 Trillion.
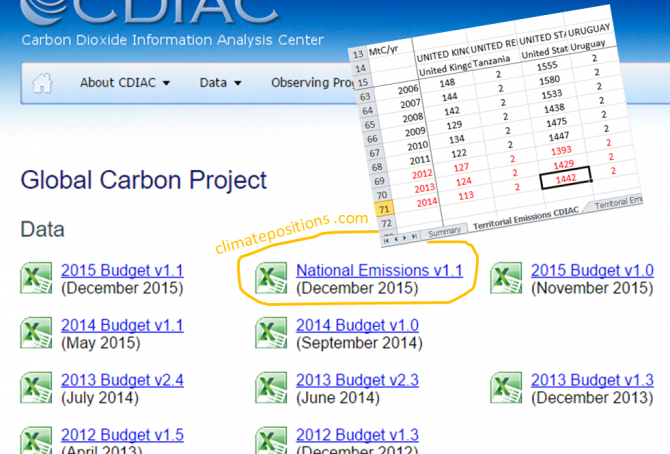
Global Carbon Project (CDIAC), located in the United States, stops publishing carbon emissions data by country – will be replaced by EDGAR in ClimatePositions
2017
The Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center (CDIAC), located at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has published annual Carbon Emissions from Fossil Fuels and cement production by country since 1959 (‘Global Carbon Project‘), but now this continuous time series has come to an end and 2015 will be the last data-year (as it seems).
Since carbon emissions data from CDIAC (Global Carbon Project) is the core ‘Indicator‘ in ClimatePositions’ calculation of Climate Debt, carbon emissions data will be replaced with nearly similar data from ‘EDGAR‘ (‘European Commission‘ / ‘Climate Action‘), retroactively since 1990, in connection with the coming updates [done 16-08-2017].
The following describes the differences between CO2 Emissions data from Global Carbon Project (CDIAC) and EDGAR (sourced: European Commission, Joint Research Centre (JRC)/Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency (PBL). Emission Database for Global Atmospheric Research (EDGAR)), and the consequences in terms of Climate Debt in ClimatePositions – illustrated with a range of country examples. Note that other sources, such as ‘IEA‘, ‘EIA‘ and ‘BP‘, provides CO2 Emissions data-sets different from the ones of CDIAC and EDGAR.
My own climate change boycott country-list
2017
Without been fanatical about it, I seek to boycott the greediest and most climate-destructive countries on the planet. For the fairness, I have divided the fifteen nominees into two leagues:
A) Countries with per capita Climate Debts more than 10 times world average: Qatar, Kuwait, Brunei, Luxembourg, Trinidad and Tobago, United Arab Emirates and Oman.
B) Countries with per capita Climate Debts between 5 and 10 times world average: Saudi Arabia, United States, Bahrain, Australia, Norway, Equatorial Guinea, Canada and South Korea.
Feel free to copy…
Among the fifteen countries only Luxembourg and South Korea are not among the world’s twenty largest per capita Fossil Fuel producers (read the article: ‘How green are the fossil fuel producers? (Correlation between fossil fuel production, CO2 Emissions, GDP and Climate Debt)‘.
The table below shows some key data of the fifteen countries. The table is read like this: 1) Between 1990 and 1999 Qatar emitted 55.1 tons of CO2 from Fossil Fuels (without bunker) and cement, annually per capita, 2) Between 2000 and 2015 Qatar emitted 51.7 tons (the average Climate Debt Free Level¹ was 32.4 tons), and 3) Qatars GDP(ppp) per capita was $143,788 in 2015.
Climate change performance: South Korea vs. Indonesia (peatlands in Southeast Asia)
2017
In 2015 South Korea and Indonesia accounted for 3.60% and 0.51% of the global Climate Debt, respectively (see the ‘Ranking‘). The following examines the ‘Indicators‘ of CO2 Emissions, GDP(ppp-$), Forest Cover (and peatlands) and Primary Forest.
The first two diagrams show the per capita CO2 Emissions from Fossil Fuel (without bunkers) and cement, annually since 2000, of South Korea and Indonesia. The green bars show the Free Emission Level¹ – the exceedance is the basis for calculating the national Climate Debt. The world’s 9th and 10th largest CO2-emitters were responsible for 1.7% (South Korea) and 1.5% (Indonesia) of global emissions in 2015, respectively. South Korea’s per capita emissions were 11.7 tons in 2015 (preliminary), while Indonesia’s were 2.1 tons (preliminary), which was 2.2% above the 2014-level.
Climate change performance: Japan vs. Germany (Renewable Energy and Nuclear Power)
2016
The world’s 5th and 6th largest emitters of CO2 from Fossil Fuel (without bunkers) and cement Japan and Germany, were responsible for 3.4% and 2.1% of the global emissions in 2015. The diagrams below show the per capita CO2 Emissions, annually since 2000. The green bars show the Free Emission Level¹ – the exceedance is the basis for calculating the national Climate Debt.
Final Update 2015: new rankings of 159 countries’ Climate Debt, accumulated since 2000
2016
Every five year, since 2005, Final Updates of national Climate Debts are completed in ClimatePositions and 2015-updates¹ are now available in ‘Calculation (Excel)‘. New rankings in six categories, of 159 countries, are available in the menu “Climate Debt”. In the coming months, the climate change performances of selected countries will be analyzed in articles, starting with the United States and China.
The following illustrate Final Update 2015 in two ways: 1) The change of Climate Debt as percentage of the global Climate Debt, annually since 2000, of the 10 largest CO2 emitters, and 2) Key-figures of the United States.
The table below of the 10 largest CO2 emitters (representing 70% of the global emissions in 2015) shows the national shares of the global Climate Debt in 2015 and 2010. China, Russia and Saudi Arabia stand out with extremely harmful developments, while the United States still has by far the largest Climate Debt. See the latest ‘Ranking’ of 159 countries.
Climate Debt: Norway ranks 9th (performance of top twenty from Human Development Index)
The so called ‘Human Development Index 2015’ (UN) ranks Norway 1st among 188 countries. The index is based on 1) Life expectancy at birth, 2) Expected years of schooling, 3) Mean years of schooling and 4) Gross national income (GNI) per capita. However, the wealthy Scandinavian oil state ‘Ranks‘ 9th among 148 countries on Climate Debt per capita. Norway is in other words a highly human developed demolisher of the climate, one might say! The following examines the climate performance of Norway in comparison with the other top five countries from Human Development Index: Australia, Switzerland, Denmark and Netherland.
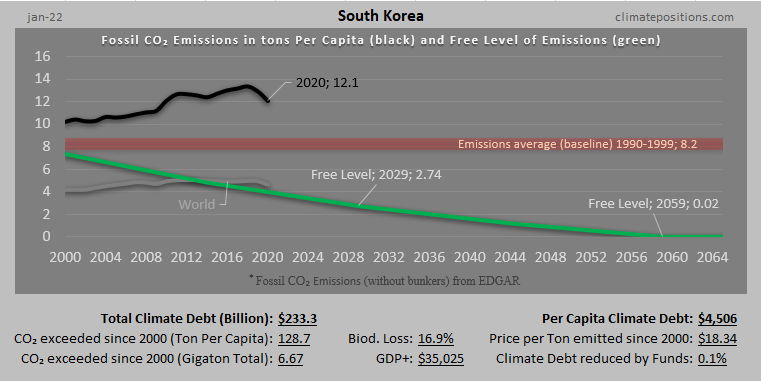
Climate Debt: South Korea now ranks 11th (Nuclear Power generation worsens the trend)
South Korea is responsible for 3.9% of the global Climate Debt of $5.7 trillion, accumulated since 2000. The per capita Climate Debt is $4,404 which ‘Ranks’ South Korea 11th among 148 countries, compared to 12th in 2010. Rankings are available in the menu “Climate Debt”. The following examines the CO2 Emissions, Nuclear Power, GDP(ppp-$) and Climate Debt, in comparison with four other large Nuclear Power generators.
The first diagram shows the South Korean per capita CO2 Emissions from fossil fuels (without bunker fuels) and cement production in decades in comparison with the world average. CO2 Emissions since 2012 are preliminary estimates. From 7.6 tons in the 1990s the level increased to 11.8 tons on average between 2000 and 2014 (preliminary). The green bars are the Climate Debt Free Level in ClimatePositions, determined by the level of emissions in the 1990s and a number of continuously updated ‘Indicators’.
Preliminary Carbon Dioxide Emissions 2014, by country
2015
’The Global Carbon Project’ at Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center (CDIAC) has published preliminary CO2 Emissions from fossil fuels and cement for 2014, for more than 200 countries. The data is being used in a preliminary calculation of accumulated Climate Debt in ClimatePositions¹. The table below shows the estimated per capita emissions plus the updated Climate Debts, of the twenty largest total emitters (responsible for 77% of the global emissions in 2014).
Analyses of the global CO2 target and GDP(ppp-$)
2015
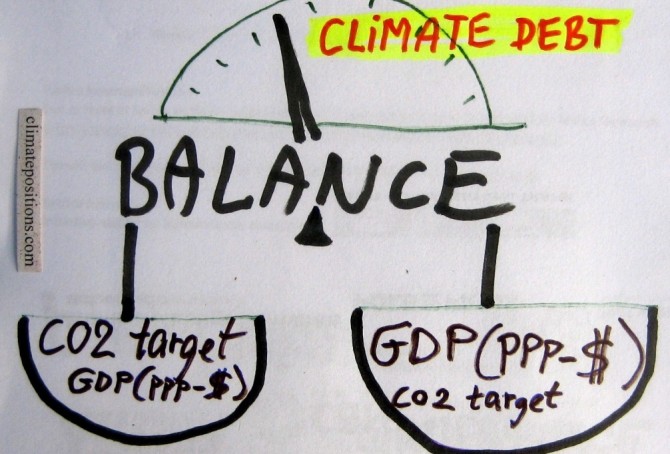
The calculation of Climate Debt in ClimatePositions is based on a balance between many ‘indicators’ and a common global per capita CO2 target. To illustrate the nature of this balance twelve countries are analyzed in this article in terms of the indicator of GDP(ppp-$) and the global CO2 target. The 12-Countries Group represents 38% of the global population, 65% of the global CO2 Emissions from fossil fuels and around 70% of the global Climate Debt.
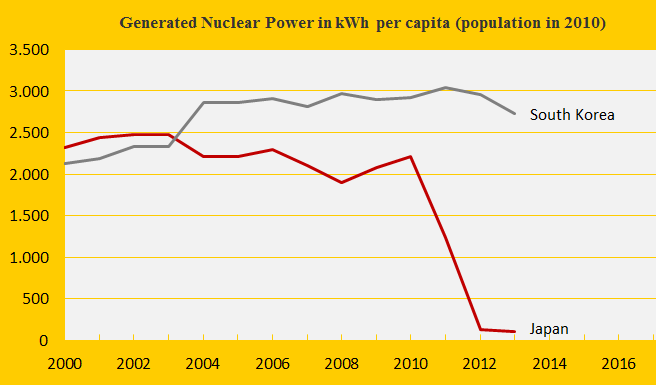
Climate change performance: Japan vs. South Korea
2014
The first diagram shows the nuclear power generation per capita of the two countries. The Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan in 2011 has caused a remarkable shutdown of generation – while CO2 Emissions from the burning of petroleum, coal and natural gas have increased (from 2011 to 2012 respectively by 6%, 5% and 3%) to close the energy gap. Nuclear power generation produce dangerous radioactive waste to deal with for thousands of future generations (10,000 to 250,000 years) and in ClimatePositions nuclear power is not accepted as a national CO2 Emission reduction instrument (read ‘more’). The following analyzes the indicator trends of Japan and South Korea.
New ranking 2014 – update of 147 countries’ climate debt
2014
The data in ClimatePositions are updated consecutively and since the data year 2010 the eleven ‘indicators’ have all been updated.
The new rankings of 147 countries are now available in the menu “Contributions” (with six categories).
All country data and diagrams are available in the menu ‘Calculations (Excel)’. In the coming months selected countries will be analyzed in articles. The following illustrates the latest updates in two ways: 1) The change of climate debt as a percentage of the global climate debt of the twelve largest CO2 emitters, and 2) The key-figures of the United Kingdom.
CO2 Emissions from flights
2014
Since the early 1990s the passenger-kilometers of flights worldwide has increased by 5-6% per year. The CO2 Emissions (carbon dioxide) per passenger kilometer vary due to difference in flight distances¹, aircrafts and load factors (percent of occupied seats) – with average load factors First Class and Business Class are causing nine- and three-times higher emissions per passenger than Economy Class, as one study suggests². Furthermore the mixed exhaust from flights causes 2-4 times more global warming than only CO2 emitted from engines on the ground³. The accumulated climate-effect from flights might be as high as 7-9% of the total effect from anthropogenic greenhouse gases4. However, the following examines only the CO2 Emissions from flights and the implied national costs in Climate Contributions (climate debt). But first see these three seductive animations (from ‘nats‘) with 24-hours flights over ‘Europe 1:59‘, ‘Middle East 1:11‘ and ‘North Atlantic 1:52‘.
Climate Contributions as a percentage of GDP for the top ten CO2 Emitters
2013
The top ten CO2 Emitters were responsible for 67% of the global CO2 Emissions in 2006-2010. Adjusting the national Contributions (climate debt) for the size of the GDP(ppp-$) is essential. Allowing the wealthy United States get away with paying the same dollar price of a ton of CO2 (carbon dioxide) exceeded as China is of course absurd. The countries’ climate change performances are measured indirectly as the Contributions’ percentage of the national GDP(ppp-$).