Climate Debt of India 2025: $66 Billion or 0.72% of the Global Climate Debt (or $46 Per Capita)
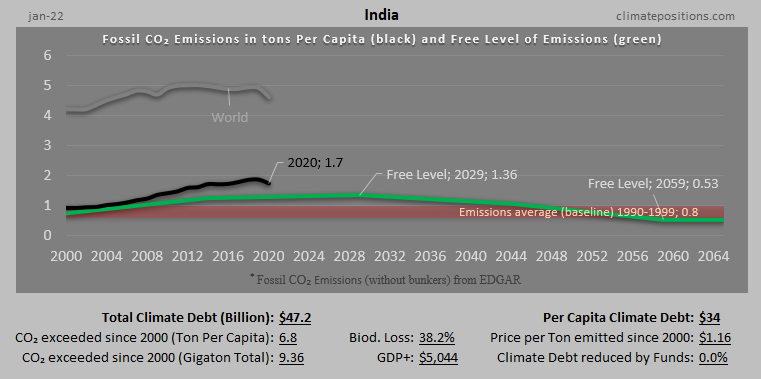
/2025/ India ranks 91st in Climate Debt Per Capita accumulated 2000-2025. Below are some key figures in the calculations. The diagram above shows the Fossil CO2 Emissions Per Capita and the Free Level of emissions (green). The wide straight red line shows emissions in the 1990s (baseline in the calculations).
Bangladesh – per capita Fossil CO2 Emissions (zero Climate Debt)
2020
Although the accumulated Climate Debt of Bangladesh is zero, the populous country is the world’s 43rd largest emitter of Fossil CO2.
The following diagrams expose the trends of Fossil CO2 Emissions, GDP(ppp-$), Environmental Performance and Population.
Pakistan – per capita Fossil CO2 Emissions (zero Climate Debt)
2020
Although Pakistan’s accumulated Climate Debt is zero, the populous country is the world’s 32nd largest emitter of Fossil CO2.
The following diagrams expose the trends of Fossil CO2 Emissions, GDP(ppp-$), Environmental Performance and Ecological Footprint without carbon.
Iran – per capita Fossil CO2 Emissions and Climate Debt
2020
Iran’s current Climate Breakdown Pricing amounts to $15.69 per tons Fossil CO2 emitted since 2000. The Climate Debt grew from $1,095 per capita in 2015 to $2,153 in 2020. Updated Rankings of 165 countries are available in the menu “Climate Debt”.
The following diagrams expose the trends of Fossil CO2 Emissions, Climate Debt, GDP(ppp-$), Ecological Footprint (without carbon) and Nuclear Power.
India – per capita Fossil CO2 Emissions (zero Climate Debt)
2020
In the calculation of Climate Debt, India is especially interesting because it has zero Climate Debt despite the fact that the country is the 3rd largest emitter of Fossil CO2. As it appears, India will enter the next 20-year period in ClimatePositions (2020-2039) without any Fossil CO2 Emissions exceeded. The final calculation will be made, when data on Fossil CO2 Emissions 2019 are released.
The following diagrams expose the trends of Fossil CO2 Emissions, GDP(ppp-$), Ecological Footprint without carbon, Forest Cover and Primary Forest.
Global indicator updates: Land-Ocean Air Temperature, Sea Level, CO2 in the Atmosphere and Population
2019
The four global Indicators: 1) Land-Ocean Air Temperature, 2) Sea Level, 3) CO2 in the Atmosphere and 4) Population, have all been updated in ClimatePositions. Combined, the updates resulted in significant increases in national Climate Debts (the first two, due to adjustments of the national GDP-Factor and the last two, due to adjustments of the global Fossil CO2 Emission target). As an example, India’s Climate Debt increased from $0.30 per capita (rounds to zero), to $2 per capita, only because of the global Indicator updates.
Diagrams with the four global Indicators are shown below.
Countries with upcoming or de facto Climate Debts
2018
Among 164 countries with full data in ClimatePositions 91 have Climate Debts. Note that Saint Lucia is new on the full data country-list with an accumulated per capita Climate Debt of $287. India, Lithuania and Latvia are likely to have small Climate Debts soon … by 2018 or 2019.
In addition to the full data country-list, 16 countries with lack of indicator data would have Climate Debts with roughly estimated data¹. The estimated per capita Climate Debts of these countries are:
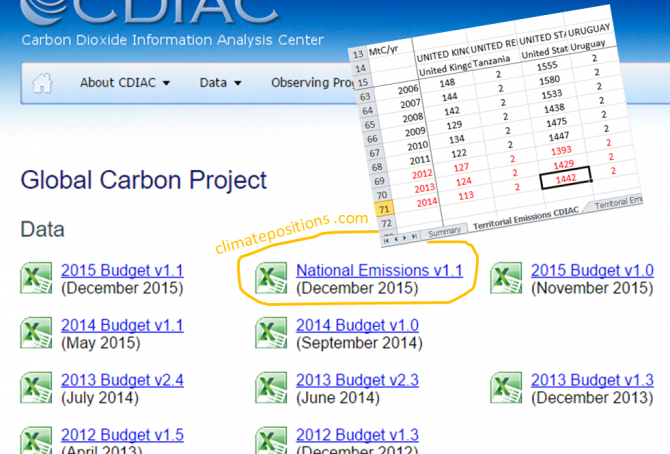
Global Carbon Project (CDIAC), located in the United States, stops publishing carbon emissions data by country – will be replaced by EDGAR in ClimatePositions
2017
The Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center (CDIAC), located at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has published annual Carbon Emissions from Fossil Fuels and cement production by country since 1959 (‘Global Carbon Project‘), but now this continuous time series has come to an end and 2015 will be the last data-year (as it seems).
Since carbon emissions data from CDIAC (Global Carbon Project) is the core ‘Indicator‘ in ClimatePositions’ calculation of Climate Debt, carbon emissions data will be replaced with nearly similar data from ‘EDGAR‘ (‘European Commission‘ / ‘Climate Action‘), retroactively since 1990, in connection with the coming updates [done 16-08-2017].
The following describes the differences between CO2 Emissions data from Global Carbon Project (CDIAC) and EDGAR (sourced: European Commission, Joint Research Centre (JRC)/Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency (PBL). Emission Database for Global Atmospheric Research (EDGAR)), and the consequences in terms of Climate Debt in ClimatePositions – illustrated with a range of country examples. Note that other sources, such as ‘IEA‘, ‘EIA‘ and ‘BP‘, provides CO2 Emissions data-sets different from the ones of CDIAC and EDGAR.
World CO2 Emissions 2000-2059: with 50% risk of 2C global warming (two per capita emission-scenarios for the United States, Denmark, Spain, China, India and Nigeria)
2017
In continuation of the previous article ‘Carbon Brief: Global Carbon Budget and CO2 Emission scenarios (50% risk of 1.5°C, 2.0°C and 3.0°C warming)‘, the following examines the per capita CO2 Emission budget 2000-2059, with a 50% risk of 2°C global warming (which of course is unacceptable). The outcome is then compared with Climate Debt Free CO2 Emission levels (in ClimatePositions) of the United States, Denmark, Spain, China, India and Nigeria, during the same 60-year period. Also, the Paris Agreements reduction commitment of the United States is put into perspective.
Climate change performance: India vs. Russia (CO2 Emissions from coal)
2016
The diagrams below show the per capita CO2 Emissions from Fossil Fuel (without bunkers) and cement, annually since 2000, of India and Russia. The green bars show the Free Emission Level¹ – the exceedance is the basis for calculating the national Climate Debt. The world’s 3rd and 4th largest CO2-emitters were responsible for 6.5% (India) and 4.9% (Russia) of global emissions in 2015. India’s per capita emissions were 1.7 tons in 2015 (preliminary), which was 4.0% above the 2014-level.
Climate change performance: China vs. the United States (wealth inequality)
2016
The diagrams below show the per capita CO2 Emissions from Fossil Fuel (without bunkers) and cement, annually since 2000, of China and the United States. The green bars show the Free Emission Level¹ – the exceedance is the basis for calculating the national Climate Debt. The world’s two largest CO2-emitters were responsible for 29% (China) and 15% of global emissions in 2015.
Apparently, China’s per capita emissions have peaked, while the moderate reduction-rate 2006-2012 of the United States, has flattened out.
Final Update 2015: new rankings of 159 countries’ Climate Debt, accumulated since 2000
2016
Every five year, since 2005, Final Updates of national Climate Debts are completed in ClimatePositions and 2015-updates¹ are now available in ‘Calculation (Excel)‘. New rankings in six categories, of 159 countries, are available in the menu “Climate Debt”. In the coming months, the climate change performances of selected countries will be analyzed in articles, starting with the United States and China.
The following illustrate Final Update 2015 in two ways: 1) The change of Climate Debt as percentage of the global Climate Debt, annually since 2000, of the 10 largest CO2 emitters, and 2) Key-figures of the United States.
The table below of the 10 largest CO2 emitters (representing 70% of the global emissions in 2015) shows the national shares of the global Climate Debt in 2015 and 2010. China, Russia and Saudi Arabia stand out with extremely harmful developments, while the United States still has by far the largest Climate Debt. See the latest ‘Ranking’ of 159 countries.
Update: GDP(ppp-$) 2015
2016
2015-updates of national per capita GDP(ppp-$) from ‘World Bank’ is now available in ‘Calculation (Excel)’. The world’s average per capita GDP(ppp-$) grew from $15,065 in 2014 to $15,470 in 2015 (2.7% growth). In the midst of an unprecedented man-made climate catastrophe and the ‘Sixth mass extinction’ in progress, the human economy keeps growing.
The diagram below shows the development in per capita GDP(ppp-$) 2000-2015 of the world’s five largest emitters of CO2 from Fossil Fuel and cement: China (27.0% of the global emissions), the United States (14.7%), India (7.2%), Russia (4.9%) and Japan (3.4%), in comparison with the world’s average.
Climate Debt: Australia ranks 8th (performance of the twenty largest coal producers)
2016
Australia covers around 5.7% of planet’s land area and populates 0.3% of its people. The Climate Debt of the 24 million Australian’s amounts to $132 billion, or $5,613 per capita, which ‘Ranks’ Australia 8th among 148 countries – in 2010 the ranking was 6th. Australia is the world’s 5th largest coal producer and the 2nd largest per capita CO2 emitter from coal combustion … and coal is the most efficient climate destroyer. The table below reveals some key figures of the world’s twenty largest coal producers. Subsequently, Australia’s climate change performance is examined in comparison with four other top-five countries on CO2 Emissions from coal combustion (per capita): Kazakhstan (ranked 1), South Africa (3), the United States (4) and Poland (5).
India’s Climate Debt is on track for something big
2016
India’s accumulated Climate Debt is $13 per capita which ranks the populous country 84th among 148 countries (see the ‘Ranking’). The current share of the fast growing global Climate Debt is 0.29%, compared to 0.04% in 2010. The following examines India’s CO2 Emissions (the increase-rates is compared to the historic Chinese rates), Environmental Performance, GDP(ppp-$) and Climate Debt in comparison with Vietnam, Morocco, Armenia and Bolivia, all ranked between 77th and 82nd.
Preliminary Carbon Dioxide Emissions 2014, by country
2015
’The Global Carbon Project’ at Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center (CDIAC) has published preliminary CO2 Emissions from fossil fuels and cement for 2014, for more than 200 countries. The data is being used in a preliminary calculation of accumulated Climate Debt in ClimatePositions¹. The table below shows the estimated per capita emissions plus the updated Climate Debts, of the twenty largest total emitters (responsible for 77% of the global emissions in 2014).
Fossil fuel subsidies: $5.3 trillion in 2015 (IMF survey)
2015
Estimates from the ‘International Monetary Fund’ (IMF) show that fossil fuel subsidies of 155 countries representing 98% of the world’s population, amounted $4.2 trillion (5.8% of global GDP) in 2011 and $4.9 trillion (6.5% of global GDP) in 2013. Projections for 2015 suggest $5.3 trillion (6.5% of global GDP). This huge amount of subsidies is of cause plain stupid.
For comparison, the total ‘Climate Debt of 147 countries‘ in ClimatePositions, accumulated between 2000 and 2013, amounted $5.2 trillion. Roughly speaking, one year of global subsidies equals the total accumulated Climate Debt. Note that global climate change funding is only around $0.14 trillion.
Estimate: India now has a Climate Debt
2015
Annual updates of ‘CO2 Content in the atmosphere’ and Global Population affects the future CO2 Emission target per capita and thus the Contribution Free Level of all countries (in ClimatePositions). The updates by January 2015 lowered India’s Contribution Free Level just enough to reach an estimated climate debt of $0.68 per capita, or a total climate debt of $812 million – the 67th largest climate debt among 146 countries or 0.02% of the global climate debt.
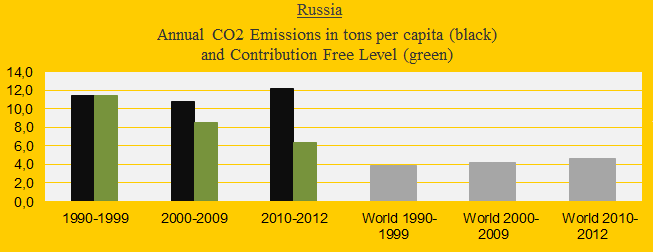
Climate change performance of Russia (compared to other BRICS countries)
2014
Russia was the 4th largest carbon dioxide emitter in 2012 with 5.6% of the global emissions, after China (26.9%), the United States (16.6%) and India (5.8%). The first diagram shows Russia’s CO2 Emissions per capita in decades in comparison with the world average (the green bars are the Contribution Free Level). After the COP summit in 2009 (at which China and the United States rejected a globally binding reduction agreement) the Russian emissions have increased dramatically and today the Russian Climate Contribution (climate debt) is $1,410 per capita (ranked 28th), compared to $627 in 2010 (ranked 32nd). See the ‘ranking’. The following analyzes the development in Putin’s Russia since 2000 in comparison with the other ‘BRICS‘ countries China, India, Brazil and South Africa – jointly emitting 41% of global carbon dioxide in 2012.