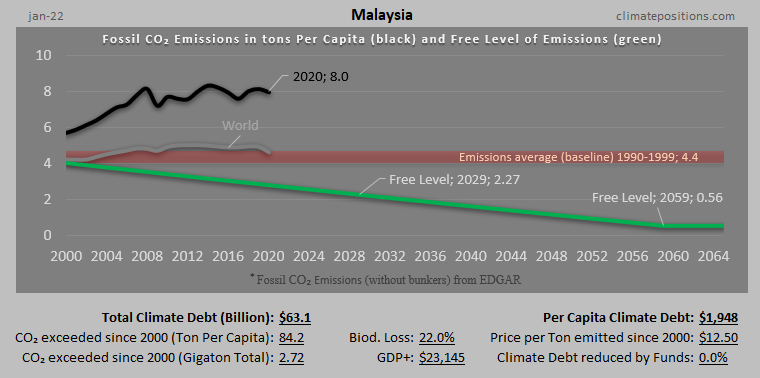
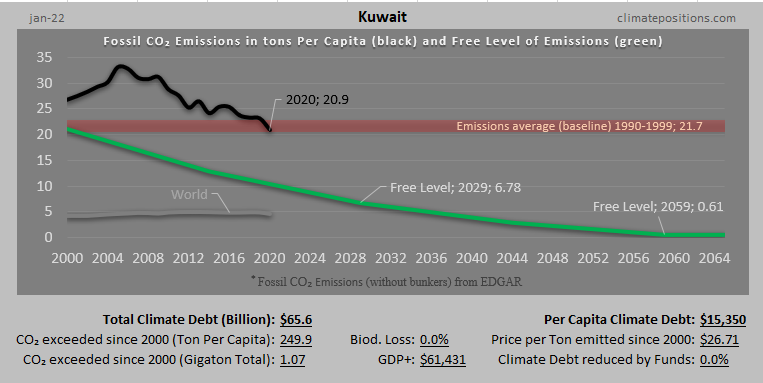
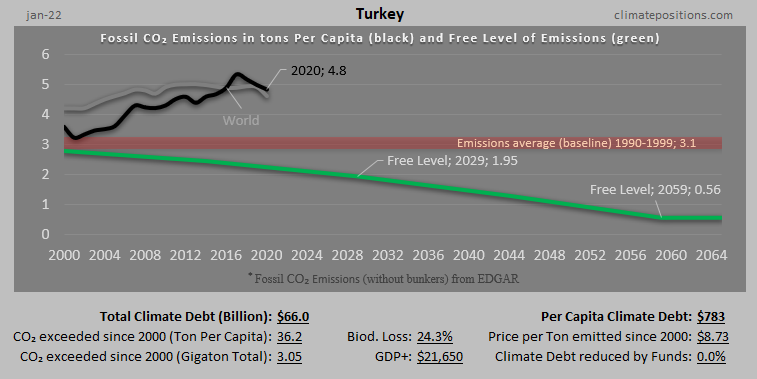
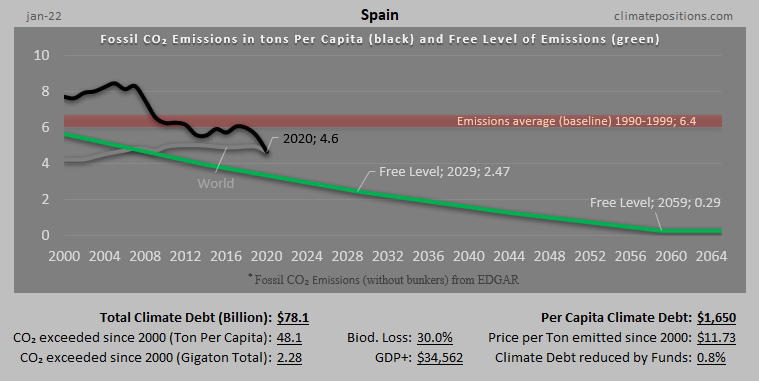
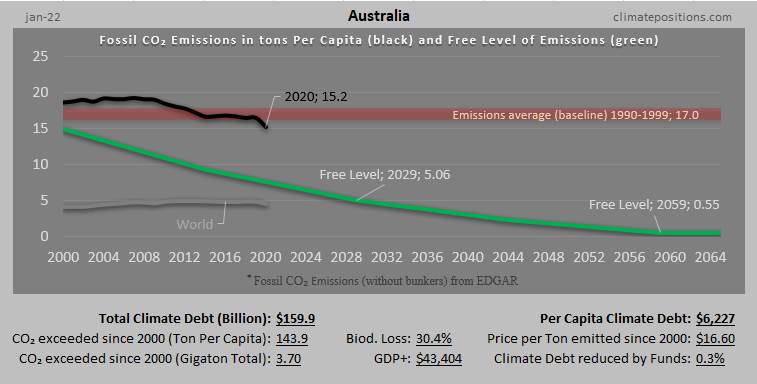
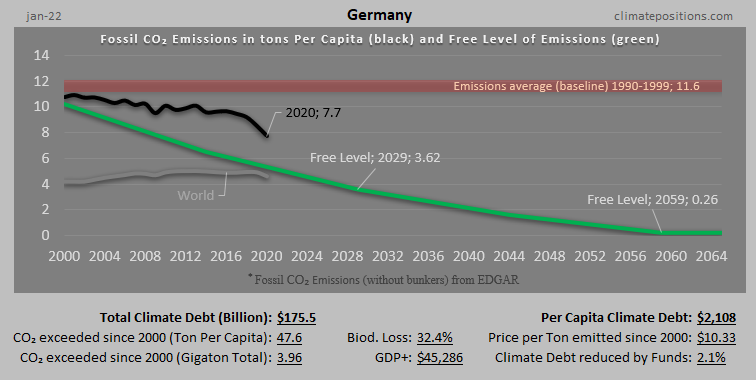
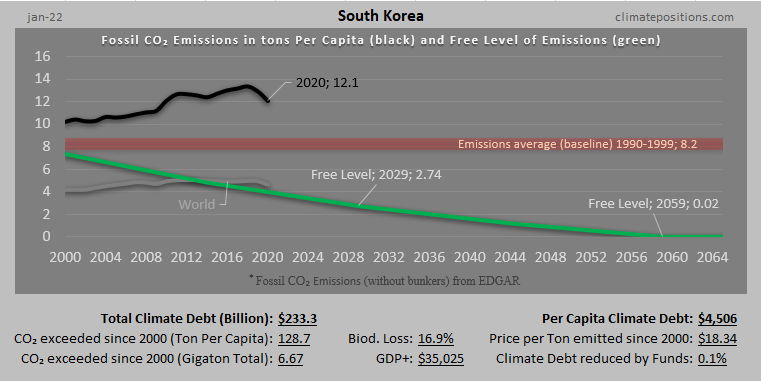
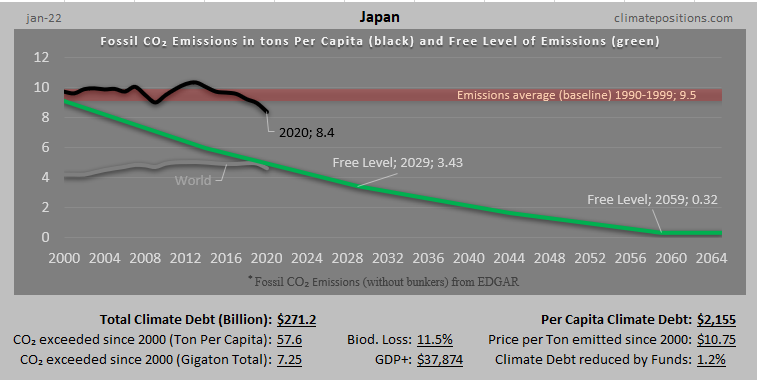
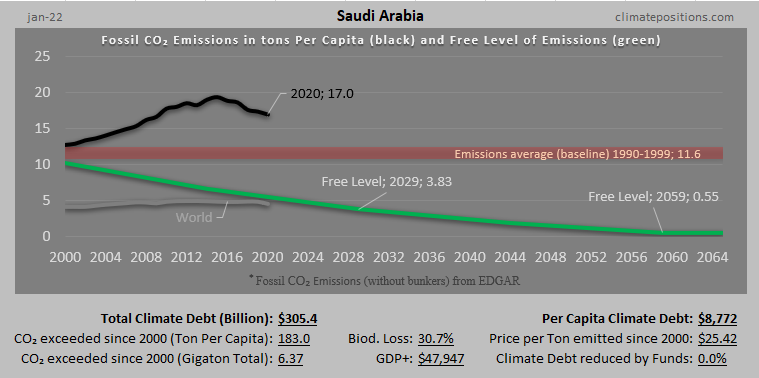
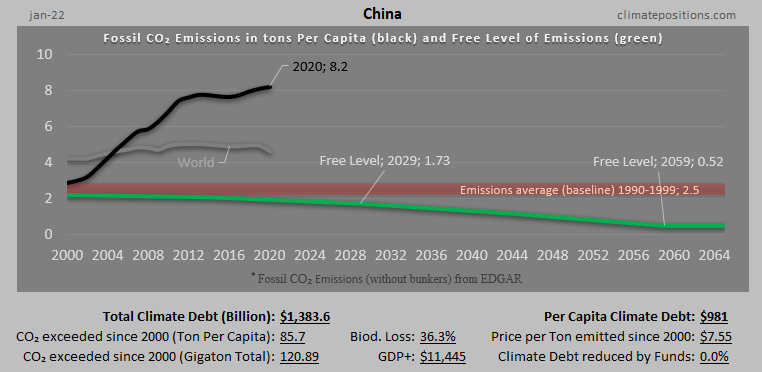
Austria – per capita Fossil CO2 Emissions and Climate Debt
2020
Austria’s current Climate Breakdown Pricing amounts to $26.30 per tons Fossil CO2 emitted since 2000. The Climate Debt grew from $2,401 per capita in 2015 to $4,371 in 2020. Updated Rankings of 165 countries are available in the menu “Climate Debt”.
The following diagrams expose the trends of Fossil CO2 Emissions, Climate Debt, GDP(ppp-$) and Ecological Footprint without carbon.
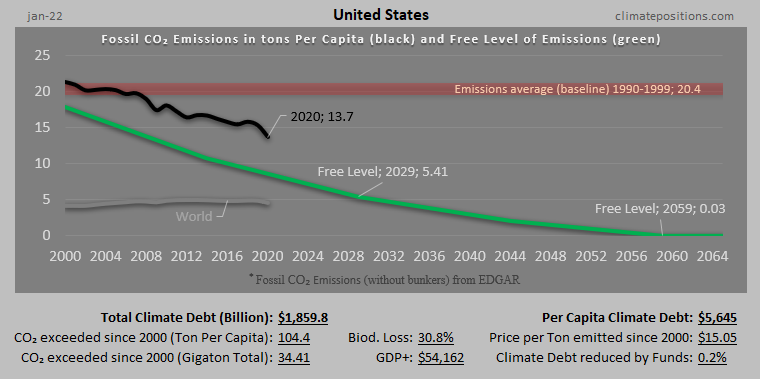
Greece – per capita Fossil CO2 Emissions and Climate Debt
2020
The current Climate Breakdown Pricing of Greece amounts to $12.76 per tons Fossil CO2 emitted since 2000. The Climate Debt grew from $1,256 per capita in 2015 to $1,929 in 2020. Updated Rankings of 165 countries are available in the menu “Climate Debt”.
The following diagrams expose the trends of Fossil CO2 Emissions, Climate Debt, GDP(ppp-$) and Ecological Footprint without carbon.